
CHECK
√
x
-
12
=
2
-
√
x
√
16
-
12
≟
2
-
√
16
√
4
≟
2
-
4
2
≠ -
2
✗
The solution does not check, so the equation has
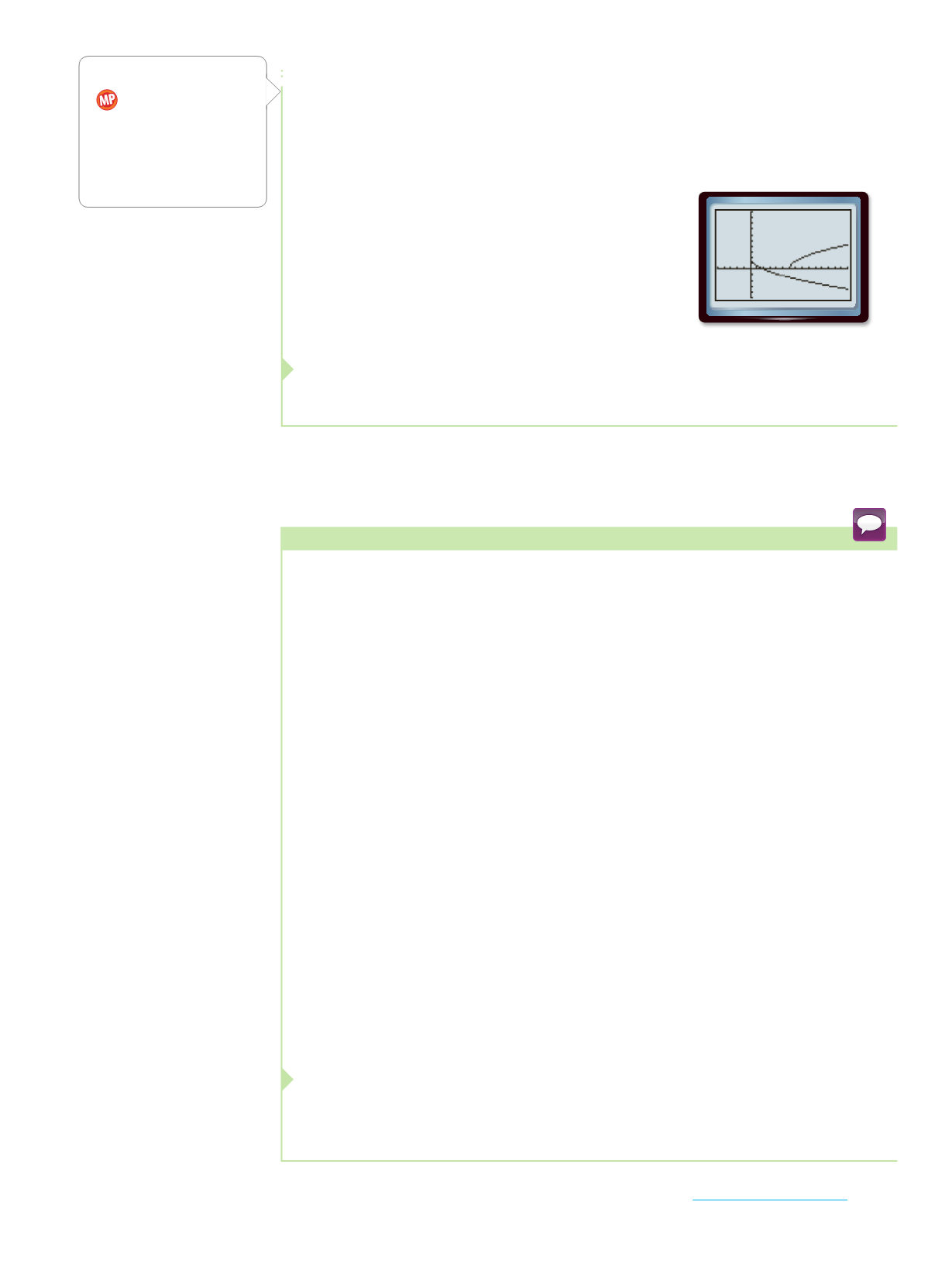
C07-029A-888482
[ 10, 30] scl: 2 by [ 5, 10] scl: 1
an extraneous solution. The graphs of
y
=
√
x
-
12
and
y
=
2
-
√
x
do not intersect, which confirms
that there is no real solution.
Guided Practice
1A.
5
=
√
x
-
2
-
1
1B.
√
x
+
15
=
5
+
√
x
To undo a square root, you square the expression. To undo a cube root, you must raise
the expression to the third power.
Solve 2(6
x
-
3)
1
_
3
-
4
=
0.
In order to remove the
1
_
3
power, or cube root, you must first isolate it and then raise
each side of the equation to the third power.
2(6
x
-
3)
1
_
3
-
4
=
0
Original equation
2(6
x
-
3)
1
_
3
=
4
Add 4 to each side.
(6
x
-
3)
1
_
3
=
2
Divide each side by 2.
(6
x
-
3)
1
_
3
⎤
⎦
3
=
2
3
Cube each side.
6
x
-
3
=
8
Evaluate the cubes.
6
x
=
11
Add 3 to each side.
x
=
11
_
6
Divide each side by 6.
CHECK
2(6
x
-
3)
1
_
3
-
4
=
0
Original equation
2
(
6
·
11
_
6
-
3
)
1
_
3
-
4
≟
0
Replace
x
with
11
_
6
.
2(8)
1
_
3
-
4
≟
0
Simplify.
2(2)
-
4
≟
0
The cube root of 8 is 2.
0
=
0
✓
Subtract.
Guided Practice
Solve each equation.
2A.
(3
n
+
2)
1
_
3
+
1
=
0
2B.
3(5
y
-
1)
1
_
3
-
2
=
0
⎡
⎣
Example 2
Solve a Cube Root Equation
Study Tip
Tools
You can use a
graphing calculator to check
solutions of equations.
Graph each side of the
original equation, and
examine the intersection.
connectED.mcgraw-hill.com353


















